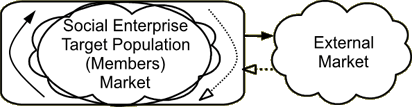
 The cooperative model of social enterprise provides direct benefit to its target population or "clients," cooperative members, through member services: market information, technical assistance/extension services, collective bargaining power, economies of bulk purchase, access to products and services, access to external markets for member-produced products and services, etc. The cooperative membership is often comprised of small-scale producers in the same product group or a community with common needs--i.e. access to capital or healthcare. Cooperative members are the primary stakeholders in the cooperative, reaping benefits of income, employment, or services, as well as investing in the cooperative with their own resources of time, money, products, labor, etc.
The cooperative model of social enterprise provides direct benefit to its target population or "clients," cooperative members, through member services: market information, technical assistance/extension services, collective bargaining power, economies of bulk purchase, access to products and services, access to external markets for member-produced products and services, etc. The cooperative membership is often comprised of small-scale producers in the same product group or a community with common needs--i.e. access to capital or healthcare. Cooperative members are the primary stakeholders in the cooperative, reaping benefits of income, employment, or services, as well as investing in the cooperative with their own resources of time, money, products, labor, etc.